Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fujita, Natsuko; Jinno, Satoshi; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Kimura, Kenji
no journal, ,
We have been developing a downsized AMS with a size of about 2 m  2 m. This AMS is developed to demonstrate a new method of separating same-mass molecules, which are interfering nuclides during AMS measurement of carbon-14, using ion channeling.
2 m. This AMS is developed to demonstrate a new method of separating same-mass molecules, which are interfering nuclides during AMS measurement of carbon-14, using ion channeling.
Hirata, Yuho; Kai, Takeshi; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
no journal, ,
Analyzing the behavior of low-energy electrons generated by radiation is vital for evaluating the response of radiation detectors. An electron track structure calculation that can analyze the electron behavior of arbitrary materials is required to investigate the response of various radiation detectors. The electron track structure calculation requires cross sections for each interaction, such as ionization and excitation. The cross sections for ionization can be calculated from binding energy and kinetic energy, for which databases are available for each element. On the other hand, excitation depends on the material's band structure, making it challenging to calculate cross sections from element-specific databases. In this study, we assume that the excitation is equivalent to the ionization of valence electrons with the band gap energy as the binding energy. Therefore, we calculate the excitation cross-section using the same method as the ionization cross-section. We have combined these cross-section calculation methods with PHITS and made it possible to calculate electron track structures using composition ratio, density, and band gap energy as input parameters. The calculated electron trajectory in Si by the developed function is consistent with the previously reported model, indicating that the developed function can analyze the electron behavior on a nanoscale.
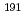 Ir
IrPatwary, K.; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Nishikawa, Takeichiro*; Yoshida, Takashi*; Horikawa, Hiroshi*; Li, G.*; Isowaki, Yosuke*; Harada, Yasuhiro*; Nagai, Yuki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Jinno, Satoshi; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Fujita, Natsuko; Kimura, Kenji
no journal, ,
We have been developing a downsized accelerator mass spectrometer dedicated to carbon-14 using a surface stripper. In order to demonstrate the practical application of  C measurement, we have performed surface scattering experiments using KCl crystals; C
C measurement, we have performed surface scattering experiments using KCl crystals; C was obliquely incident on the KCl crystals, and the rate of charge conversion of specularly reflected particles was calculated. In addition, we adjusted the beam of positive ions after charge conversion, detected dissociated fragments downstream of the analyzing magnet, and confirmed the operation of the ion detector with proportional counters.
was obliquely incident on the KCl crystals, and the rate of charge conversion of specularly reflected particles was calculated. In addition, we adjusted the beam of positive ions after charge conversion, detected dissociated fragments downstream of the analyzing magnet, and confirmed the operation of the ion detector with proportional counters.
 Sr in environmental samples utilizing laser photo-detachment
Sr in environmental samples utilizing laser photo-detachmentHonda, Maki; Martschini, M.*; Marchhart, O.*; Steier, P.*; Golser, R.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*
no journal, ,
Accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is a relatively new analytical chemistry in applied research utilizing accelerators. In Japan, AMS has been used to measure  C, which is applied for dating in archaeology, and
C, which is applied for dating in archaeology, and  Cl, which is used to assess the environmental effects of the disposal of radioactive waste from nuclear power plants and accelerator facilities. In recent years, conventional AMS systems have been combined with new analytical chemistry techniques to separate isobars, such as laser photo-detachment, leading to improved performance and the possibility of measuring new nuclides in AMS. This presentation will mainly focus on developing a highly sensitive
Cl, which is used to assess the environmental effects of the disposal of radioactive waste from nuclear power plants and accelerator facilities. In recent years, conventional AMS systems have been combined with new analytical chemistry techniques to separate isobars, such as laser photo-detachment, leading to improved performance and the possibility of measuring new nuclides in AMS. This presentation will mainly focus on developing a highly sensitive  Sr analysis technique utilizing the laser photo-detachment method equipped in the 3MV AMS at the University of Vienna. Furthermore, the feasibility of
Sr analysis technique utilizing the laser photo-detachment method equipped in the 3MV AMS at the University of Vienna. Furthermore, the feasibility of  Sr AMS at facilities in Japan will be discussed.
Sr AMS at facilities in Japan will be discussed.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Matsushima, Hisayoshi*; Yano, Masahiro; Terasawa, Tomoo; Asaoka, Hidehito; Jessiel, G.*; Wilson, D.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
no journal, ,
In this study, hydrogen isotope separation ability of graphene was investigated by using electrochemical and theoretical approaches. We found that graphene exhibits high separation ability (H/D) and its bias dependence, and theoretical analysis showed that bias dependence of H/D results from a transition from the quantum tunneling regime to the classical over barrier regime for hydrogen isotopes transfer through the graphene. The findings will help us understand the origin of the isotope separation ability of graphene discussed so far and contribute to developing an economical hydrogen isotope enrichment system using two-dimensional materials.
 In induced by grazing-incidence neutrons on an InP substrate measured as a function of neutron glancing angle
In induced by grazing-incidence neutrons on an InP substrate measured as a function of neutron glancing angleYamazaki, Dai; Mizusawa, Mari*; Moriai, Atsushi; Takeda, Masayasu; Matsue, Hideaki; Sakurai, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Nogami, Mitsuhiro*; Hitomi, Keitaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Twelve years have passed since the 1F accident that occurred in 2011, and contaminated soil generated in Fukushima Prefecture is being managed as removed soil. We have focused on the functionality of several crystalline minerals obtained in the process of developing a technology to remove Cs from the removed soil, and are examining their potential as thermoelectric conversion materials. In this study, we report on the evaluation of thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and Seebeck coefficient) of the crystalline minerals.
Takabayashi, Susumu*; Fukuda, Akito*; Tsukazaki, Ryuta*; Koga, Hisashi*; Yamaguchi, Hisato*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Takakuwa, Yuji*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Graphene has a wide variety of potential applications, including as a channel material in field-effect transistors and as a gas barrier film. The chemical modification and reformation of graphene was studied using photoemission-assisted plasma. In the C 1s photoelectron spectra of graphene/Cu substrates treated under Townsend discharge conditions, which prevent ion damage, both sp2 carbon (sp2 C-C, sp2 C-H) of graphene and a sp3 carbon (sp3 C-H) were observed by synchrotron radiation XPS, indicating that the six-membered ring structure of graphene was cleaved and hydrogen was bonded to it. On the other hand, annealing in a hydrogen-reducing atmosphere resulted in the disappearance of the sp3 C-H and sp2 C-H peaks and the appearance of the sp3 C-C peak, corresponding to hydrogen desorption.
 (001) surface
(001) surfaceKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Kim, K.*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Inami, Eiichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abe, Masayuki*
no journal, ,
NOx-based gases emitted from engines and plants are an important issue from an environmental perspective. For the detoxification of NO, it is important to understand its reactivity and reaction mechanisms. The reactivity of anatase TiO (001) which is a highly active photocatalyst was studied by using NO supersonic molecular beams and synchrotron radiation XPS. It was found that the N1s peak was observed, indicating that the surface without surface cleaning reacts with NO molecules.
(001) which is a highly active photocatalyst was studied by using NO supersonic molecular beams and synchrotron radiation XPS. It was found that the N1s peak was observed, indicating that the surface without surface cleaning reacts with NO molecules.
Qiao, Y.*; Arai, Taiki*; Suzuki, Toshiaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Niwa, Masaaki*; Motohashi, Mitsuya*
no journal, ,
Roll-like structures with a thickness of about 1  m fabricated by anodization of the surface of single-crystalline Si wafers have the potential to be applied to a variety of devices. With the aim of controlling the thickness and length of the rolls, the influence of the surface condition of the Si substrate before anodization was investigated. It was found that Pt coating before anodization was effective in controlling the thickness of rolls. Furthermore, it was found that this result was not affected by the doping types.
m fabricated by anodization of the surface of single-crystalline Si wafers have the potential to be applied to a variety of devices. With the aim of controlling the thickness and length of the rolls, the influence of the surface condition of the Si substrate before anodization was investigated. It was found that Pt coating before anodization was effective in controlling the thickness of rolls. Furthermore, it was found that this result was not affected by the doping types.